RobustNet [Eng]
Yizhou et al. / Revisiting the Transferability of Supervised Pretraining an MLP Perspective / CVPR 2022
1. Problem definition
Many recent unsupervised learning method paper shows much better transferability than supervised learning method with cross entropy loss on a number of tasks, e.g. object detection, sematic segmentation. Untill now no one has given a resonable explanation of why unsupervised pretraining outperform supervised pretraining.
In this paper, the author shed new light on understanding the transferability gap between unsupervised and supervised pretraining from a multilayer perceptron (MLP) perspective.
2. Motivation
Related work
1. MLP in unsupervised learning methods. A lot of papers show that adding a multilayer perceptron (MLP) projector at the bottom of the encoder can significantly improve the performance. The first paper introduces this component is SimCLR and they provide a working therom from reducing the information loss caused by the contrastive loss. However, how the reason why MLP can improve the model transferability is under-known.
2. MLP in supervised learning methods Recently, several works try to apply MLP and contrastive loss on supervised learning in order to improve its transferability. But all of those works did not try to ablation the effect bringing by the MLP projector and claim that the improvement is caused by introducing contrastive mechanism.
Idea
The main idea of this work is that they find that the transferability improvement is mainly caused by the adding projector. The author illustrate that, by adding an MLP projector, supervised pretraining methods can have comparable or even better transferability than representative unsupervised pretraining methods. After attributing the contribution of projector the author provide an theoretically proof by preserving intra-class feature variation.
3. Method
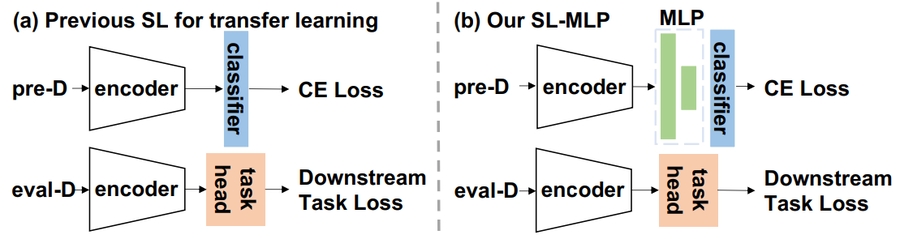
The above figure shows the difference between conventional supervised pretrain-transfer learning (SL) and the proposed MLP adding method (SL-MLP) which is simply add one MLP layer after the encoder network.
4. Experiment & Result
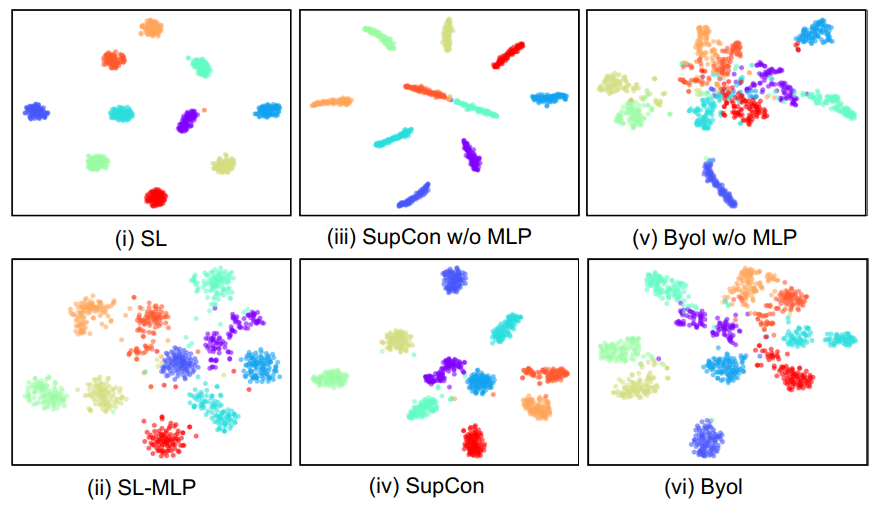
As shown in the above figure features extracted by pretrained models without an MLP projector (top row) have less intra-class variation than those extracted by pretrained models with an MLP projector (bottom row).
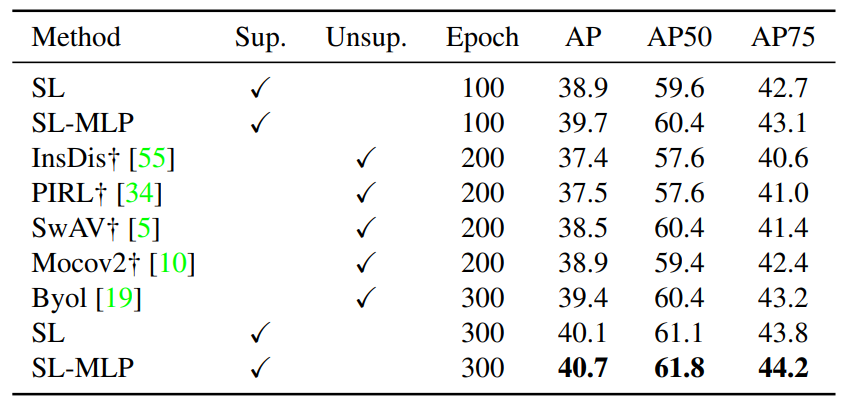
Using ImageNet-1K to pretrain, the table shows the result of finetuning on COCO dataset with Mask-RCNN (R50-FPN) based on Detectron2. We can see a significant improve comparing to self-supervised method (Mocov2, SwAV).
Experimental setup
The model is pretrained on ImageNet-1K and then evaluates the transferability on COCO dataset with the code from Detectron2.
5. Conclusion
This paper find out the truly reason of why previously work can improve the supervised training model can achieve higher transfer performance, which bridge the gap between supervised and unsupervised pretraining. They empirical find the main factor lies on the adding MLP projector.
Take home message (오늘의 교훈)
In supervised training, simply add an MLP layer after the main network can dramatically improve the transfer learning ability of the network.
Last updated